Formaldehyde is common chemical used in multiple industrial and household applications, though historically it has been a specialty chemical for quite a long period of time due to the lack of its main feedstock, methanol. Formaldehyde is mainly used to manufacture formaldehyde-based resins, specifically urea-, phenol- and melamine-formaldehyde resins. This application area accounts for nearly 70% of formaldehyde output globally. Its uses also include various chemicals (BDO, MDI, polyacetal and pentaerythritol), embalming agents, crease-resistant fabrics, wallpaper, paints, gasoline stabilizers, drying agents, preservatives in cosmetics, and biocides in metal machining fluids. Most formaldehyde is produced and sold as formalin (37% formalin), an aqueous solution of formaldehyde with some methanol.
Since formaldehyde-based resins and its derivative chemicals act as intermediates or end-products for other industries, the global and regional formaldehyde markets depend from behaviour of these industries and sectors, thus forming a complex network of interdependences and causal feedback loops. For instance, formaldehyde resins are used as adhesive and binding ingredients in various engineered timber products, including MDF, OSB, particleboard, plywood and laminated products, which are heavily linked to construction (e.g. flooring, spray foam insulation), remodeling, furniture production, etc. The behaviour of the construction sector largely hinges on the macroeconomic situation or occurrence of force majeure circumstances. For instance, Hurricane Katrina led to a great need in wood products with large formaldehyde content. Later, wooden trailers with formaldehyde-containing wooden panels became a subject of serious investigation, when they caused multiple adverse heath effects.
Thus, the general trend of the formaldehyde market development during some time interval arises from the interplay of different factors (attenuating and reinforcing its growth), whose dynamics is non-linear and complex.
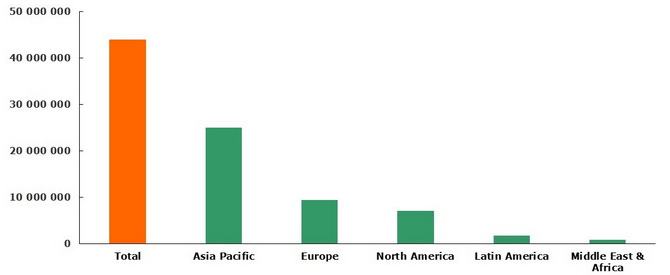
In similar vein, recent economic slowdown in China inevitably impacts the Chinese construction and furniture sectors, while robust consumption environment may denote a balancing feedback, but concerns over the safety of formaldehyde in pressed-wood and composite wood products exported from China may reinforce negative trends in the Chinese formaldehyde sector, as the US Environmental Protection Agency is seriously inclined to stringently regulate formaldehyde use. Formaldehyde, which belongs to a family of chemical compounds called volatile organic compounds (VOCs), is known to demonstrate a number of adverse health effects and long-term exposure to high levels of formaldehyde has been associated with cancer in humans and laboratory animals. Its use is therefore regulated by a number of standards. The EPA’s steps to tighten formaldehyde application standards may be worrying for China, which accounts for 52% of global formaldehyde production, though European and North American sectors might be influenced too. European share in global forlmaldehyde production was almost 21.2% in 2014, and North America accounted for about 16%.
Formaldehyde: structure of the global production broken down by region, 2014 (tonnes)
More information on the formaldehyde market can be found in the in-demand research report “Formaldehyde 2015 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2019”.
