Ammonia is an important chemical, which lies at the foundation of the whole nitric industry. It has multiple applications but the central one is the production of liquid nitric fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate, urea or aqua ammonia. Its importance for the fertilizer sector hinges on its versatility: it can be used in direct application or as a component of other nitric fertilizers.
The global market for ammonia is bullish, mature, balanced, tight, and full of competition. If viewed from historic perspective, its output growth pace has been amazing. Backed by the advances of the Green Revolution and demographically caused fertilizer gluttony, the production of ammonia grew from 8 mln tons in 1955 to over 170 mln tons in 2013.
Being produced in over 80 countries and by multiple companies, the ammonia market encounters with severe competition. However, this competition is somewhat mitigated by the fact that the amount of ammonia entering the global trade is not that big, around 11-12%, while the bulk of this product is processed or consumed domestically within manufacturing countries (the amount of many ammonia-based derivative products, like urea, entering global trade is much bigger than 12%). This competition takes its toll in the form of robust M&A activities, market escapes or company stake sales, which might not be directly related to competitor actions but is nevertheless associated with them. For example, Borealis Chimie has recently sold its stake in urea production and ammonia storage plants in France to Yara in accordance with its business optimization strategy.
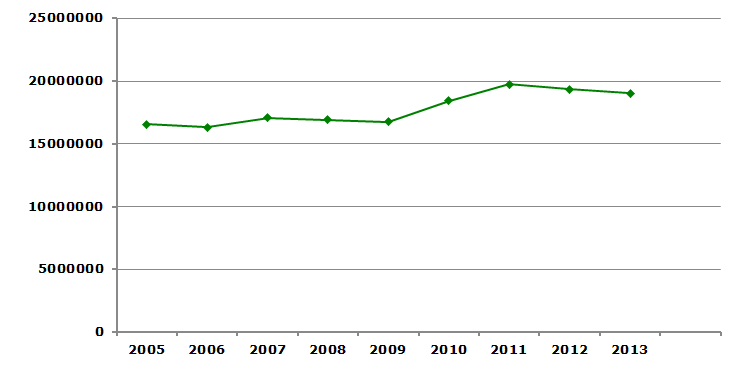
However, expansions and new projects make up a much stronger trend with multiple projects planned ahead. Whether each and every new plant and expansion project being pursued today goes into production in future is debatable, the capacity increases are significant. For example, North America, which is not the biggest market for ammonia with just 9-10% in global ammonia production, plans to expand annual ammonia capacity by 6.65 million tons from 2014 to 2018, which might be a direct route to excessive supply and reduced margins. According to Yara representatives in North America, there exists a significant risk of future nitrogen over-supply in North America. If one looks at almost stagnant ammonia consumption growth in North America between 2005 and 2013 and ever-present peril of gas price hikes, the risk associated with such a capacity boost is evident.
Ammonia consumption in North America in 2005-2013, tons
For example, in 2003, PotashCorp’s facility in Geismar, LA was forced to shut down ammonia production due to escalating natural gas prices (in 2011, the company announced plans to resume ammonia production at this plant).
The recent SWOT-analysis of major ammonia manufacturers (Yara, CF Industries, Hubei Yihua Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., PCS Nitrogen, Qatar Fertiliser Co, and Koch Fertilizer) revealed that the major ammonia market drivers included supply and demand interactions, macroeconomic and financial conditions, trade policy of separate countries, environmental regulations, seasonality and some other factors.
More information on the ammonia market can be found in the in-demand research study “Ammonia: 2015 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2019”.
