The use of methanol and its blends as a fuel is determined by a number of their strengths. These strengths may include attractive prices as compared to gasoline, ethanol and their blends; simplified applicability without significant modification of methanol-running engine; relatively smaller toxicity with decreased particulate matter. Methanol is also used as a key component in the development of different types of fuel cells since methanol is an ideal hydrogen carrier. The matter of concern could be its toxicity.
Methanol market behaviour is highly volatile: it is one one of the basic chemicals, incorporated into many downstream and upstream production/commodity chains, market systems and application areas (related to such enormous sectors as chemical industry, transportation and energy). Such complexity makes this volatility inevitable and dependable on a number of factors and dimensions, like seasonal factors, regulation or regional aspects.
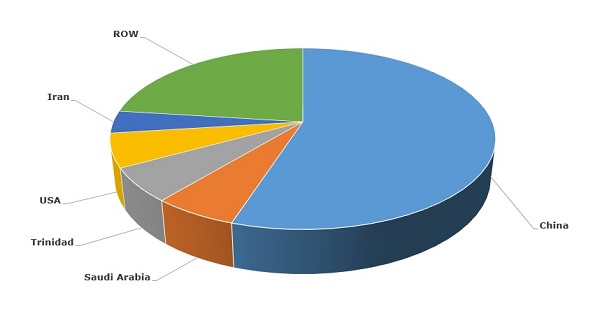
Methanol: structure of the global production by country, 2015
The current (Jan-Feb of 2017) rise in methanol prices and margins might be considered a short-term seasonal event or a longer trend. Despite methanol capacity additions (described below), there are also large increases in methanol consumption, like new methanol-to-olefins plants, coupled with rises in methanol-producing feedstock, especially in many coal-based Chinese facilities. However, it is highly possible that the present increase in demand will be relatively soon covered by the launch of new methanol capacities in different parts of the world in 2017 and 2018. New methanol facilities are planned in the USA (the major projects are planned by Yuhuang Chemical Inc. and Natgasoline LLC in 2018 and 2017), Russia (by Metasev and LLC Baltic Gas Chemical Company, both projects to be realised in 2019), Nigeria (Brass Fertilizer Company Ltd. in 2018), China (Gansu Pingliang Hua Hong Hui Jin Coal Chemical Co. Ltd and China Wlson (Nanjing) Clean Energy in 2017), Trinidad, Poland, Iran, Bolivia, Mozambique and other countries. Of course, with increased recent economical, corporate and political uncertainty, some of these projects may be delayed or even cancelled for different reasons. However, methanol capacity additions seem to be sufficient to cover the growing demand (driven by such new applications areas as methanol-to-olefins (MTO), DME and direct gasoline blending), whose dynamics will also follow macroeconomic situation.
More information on the methanol market can be found in in-demand research repot “Methanol: 2017 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2021”.
