Methanol is an important chemical commodity with versatile and prospective applications, including power generation, transportation, and chemical industry. In the chemical industry, methanol is used to manufacture a wide range of chemicals via the methanol-to-olefins process.
Among other things, the prospective status of methanol application stems from its capacity to be produced from biomass, waste and renewable energy sources like carbon capture schemes. For instance, BASF, with its long tradition of innovation in methanol production, has launched an EU-REDcert-methanol on the basis of its proprietary biomass balance approach. The biomass balance approach is a new strategy of raising the use of renewable feedstock-based chemicals; it is also a marketing opportunity for BASF to increase the base of its clients who are interested in improving general sustainability of chemical production. The approach implies the use of renewable raw materials (bionaphtha and biogas) at the very early stages of the production chain. The bionaphtha is added to the standard naphtha, which creates “a mix” of bio-based and fossil-based feedstock. Then, after the final products (methanol or other selected commodities) are manufactured, they are certified according to the REDcert standard. In the certification process, a mathematic calculation of the bio-based feedstock proportion in the total mix is considered. REDcert is a standard for biofuel use, which acts in compliance with the EU’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED). With this technology, BASF performs the replacement of fossil raw materials with the corresponding quantity of renewable raw materials at the beginning of the production process. The resultant EU-REDcert-methanol has the same formulation and quality as the end-product manufactured exclusively from standard naphtha.
Other possible innovations in methanol industry may lie in its application in internal combustion engines (methanol does not require significant modification of methanol-running engine), as well as in direct methanol fuel cells. China, which is the world’s largest producer of methanol (in 2018, China produced 47.6 mln tonnes of methanol), actively supports the technology of using methanol as a transport fuel. Its major automaker, Geely Auto, has recently launched a factory that can make 300,000 methanol-fuelled cars a year in southwestern Guizhou province. Currently, Geely has developed four methanol engines to be installed at 14 methanol models.
Methanol: structure of the global production by country
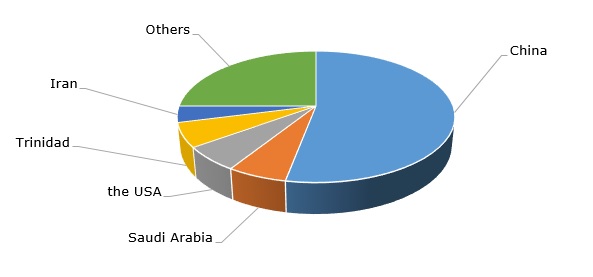
New methods of methanol production are also a prospective area of innovation. These methods may address the issues of raising energy efficiency at methanol production or the use of methanol in its hydrous “raw” form, which may offer significant cost reduction.
More information on the global methanol market can be found in the in-demand research report “Methanol: 2019 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2028”.
