Acrylonitrile (CAN) is an important monomer used for the production of acrylic fibres, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) resins, and water-soluble polymers. The versatility of these product groups employed in a vast range of applications raises the commercial status of acrylonitrile. However, unlike PP, LDPE/HDPE or PVC, acrylonitrile-based plastics (e.g. ABS in which acrylonitrile is a key component) are not the main types of plastics used worldwide.
Numerous researches have failed to confirm that acrylonitrile-based plastics demonstrate toxicity under correct conditions of exploitation. Nevertheless, acrylonitrile itself could be possibly carcinogenic to humans according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer. This effect of acrylonitrile was observed in tobacco smoking where acrylonitrile was present among multiple volatile organic compounds. Another detrimental effect of acrylonitrile upon the environment occurs within the framework of the general pollution of the surroundings with plastic wastes. This relates to the global issue of environment pollution with plastics. As a result, the development of effective plastic-recycling and utilization technologies is paramount.
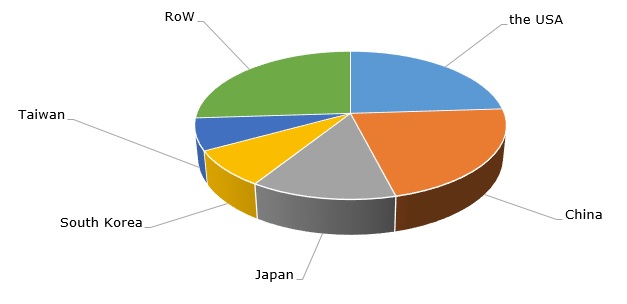
As acrylonitrile toxicity is an issue in specific applications, the general pollution of the environment with plastic (like ABS) derives from large volumes of plastic output based on its overconsumption. In general, the annual acrylonitrile output exceeds 7 mln tonnes with major acrylonitrile-producing centres located in the USA, China, and Japan.
Major acrylonitrile-manufacturing countries
Despite significant European acrylonitrile capacities (18% of the global capacities), they are scattered, though just a few big players dominate the market. In Europe and worldwide, Ineos is one of them, being the world’s largest acrylonitrile producer, owning over 1.3 mln mty of acrylonitrile capacity. Actually, the acrylonitrile-manufacturing technology developed by this company accounts for over 90% of all acrylonitrile produced globally. It is one-step, fluid bed acrylonitrile manufacturing process, which was developed by scientists of The Standard Oil Company (Sohio), one of INEOS’s predecessors in the U.S. Naturally, when the Ineos’ acrylonitrile production in Europe is affected, it immediately feedbacks on the whole European acrylonitrile market. For instance, in H2 2018 and Q1 2019, Ineos encountered with a series of force majeure circumstances at its plants in UK and Germany (its US plant in Texas had similar issues at about the same time). Multiple reasons were involved to cause force majeure declaration, including power cuts (at the plant in the UK in early June 2018), feedstock ammonia supply disruptions (at the plant in Germany in late February 2019) and operational failures (at the plant in Germany in early June 2018). All these factors resulted in the rise of the European acrylonitrile prices.
More information on the global acrylonitrile (CAN) market can be found in the in-demand research report “Acrylonitrile (ACN): 2019 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2028”.
