Dioctyl phthalate [synonyms: DOP; bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate; DEHP] belongs to the class of phthalic acid esters (PAEs), which are mainly used in plasticizer-related applications in polymer products. Plasticizers are vital organic additives to polymers. Plasticizers are able to modify flexibility, hardness, viscosity, swelling, processability, and other properties of final polymer products. This opens up good opportunities for plasticizer application, especially in such essential areas as the manufacture of medical and sanitary products (e.g. blood bags, dialysis equipment, inhaler filters, bioreactors and bioreactor bags used for vaccine development, drug delivery systems, medical tubing, N95 facemasks, cleaning solutions, disinfectants, etc.).
However, the use of dioctyl phthalate, which generally belongs to the phthalates family of substances, is tarnished by the proven record of its toxicity and multiple adverse effects for human health and the environment. Various studies during the last two decades (including the most recent ones as of 2020) confirm the capacity of dioctyl phthalate and other phthalates to induce reproductive and developmental toxicities, pathological alterations on the hippocampus, neurotoxicity, obesity, low birth weight in infants, autism, negative impacts upon endocrine and thyroid hormone systems and other detrimental effects. The situation is exacerbated by phthalates occurrence in water, air, and food, as well as their resistance by microbial decomposition. Overall, children are more exposed to phthalates than adults. These facts pose a most serious threat to the dioctyl phthalate market development. They became the reason for including 8 phthalates, [among them are di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and di-n-octyl phthalate (DnOP)], in the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) management plan in 2012. The plan initiated action to address the manufacturing, processing, distribution in commerce, and/or use of these eight phthalates.
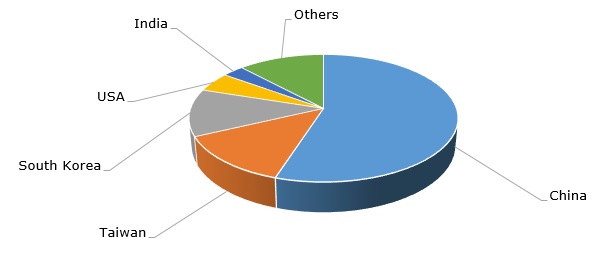
However, the US share of the global dioctyl phthalate market capacity is rather small – about 5%, while the market is heavily dominated by the Asia Pacific region, where environmental regulation is far from being very strict, though the general trend for imposing a tighter control over phthalate exposure in Asia Pacific countries is obvious.
Dioctyl phthalate (DOP): structure of the global production capacity by country
Currently, the market for dioctyl phthalate slowly recovers when multiple production facilities resume their operation after the cancellation of numerous Covid-19 lockdowns, though the pandemic is far from over with the brunt of it being transferred to India and South American countries. The market remains sluggish, while prices for dioctyl phthalate could hardly show an upward trend in the nearest future. For instance, a year ago prices for dioctyl phthalate manufactured by Eastman at its 230k mty facility in Kingsport demonstrated a steady growth, which is unlikely in the current business environment. Eastman’s dioctyl phthalate is used in flexible PVC resins, garden equipment, gaskets, etc. Just on the contrary, Eastman’s non-phthalate plasticizers are presently in high demand as essential intermediates to be used in the medical, food supply, and cleaning applications, including those to combat Covid-19 impacts.
Of course, the upward pressure on dioctyl phthalate prices may be rendered by the rising prices for phthalic anhydride, which is in turn obtained from substances such as oxylene or naphthalene. It is expected that general manufacturing costs may rise due to various factors. Of course, the dioctyl phthalate market will be supported by the fact that it is the most extensively used plasticizer in plastics processing and it still leads the demand for plasticizers for PVC production.
More reliable information on the global dioctyl phthalate (DOP) market can be found in the comprehensive research report “Dioctyl Phthalate (DOP): 2020 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2029”.
