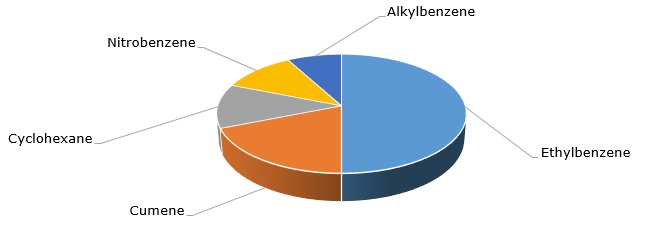
Industrial manufacture of nitrobenzene began in the mid-19th century. Acting as an intermediate, it is tightly coupled with aniline and other downstream products since 95% of produced nitrobenzene is used for aniline production. Upstream-wise, nitrobenzene is the fourth largest outlet for benzene consumption, following ethylbenzene, cumene, and cyclohexane. The nitrobenzene segment is the fastest-growing outlet for benzene consumption.
Benzene: structure of the global consumption
Aniline’s main use, accounting for over 70% of its consumption, is in the production of methyl di-p-phenylene isocyanate (MDI), primarily used in rigid polyurethane (PU) foams. Other aniline end applications include sectors as diverse as construction (over 30%), rubber products (12%), transportation (10%), consumer products (10%), adhesives/sealants (8%), packaging (5%), agriculture (4%), textiles (3%), coatings (3%), photography, pharmaceuticals, electronics and pulp and paper. As such, the behaviour of the global nitrobenzene market mirrors fluctuations of the global market for aniline, which is in turn affected by the above aniline consumption markets. Key nitrobenzene manufacturers, therefore, pair nitrobenzene production with that of aniline.
Nitrobenzene has a number of direct applications, like in machinery lubricants, perfumery to mask harsh odours, synthetic rubber, dyes, plant growth stimulants, and drugs such as acetaminophen. The latter makes nitrobenzene particularly valuable now as acetaminophen is a drug recommended by the WHO to reduce fever and pains in people with symptoms of any viral infection, including Covid-19. However, it is clear that only a modicum of nitrobenzene is used for this application.
The current state of the nitrobenzene market is adversely influenced by the economic recession caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, though the global economy is slowly recovering. The nitrobenzene market remains subdued. The situation is exacerbated by a possibility of the second wave of Covid-19, like the one which is now occurring in Texas, where there is an upsurge in new Covid-19 cases. The latter occurrence may pose a serious threat for petrochemical complexes located in the area, especially for the aniline facility operated by Dow Chemical in Beaumont, Texas (Dow bought this facility from Chemours in 2015).
Major nitrobenzene/aniline manufacturers (Huntsman, Chemours, Dow, BASF, etc.) are multinational vertically integrated chemical companies that are highly flexible in their operation. These companies operate large integrated chemical complexes, such as BASF’s complex in Chongqing, China, which has a capacity of 400,000 mty of nitrobenzene, 300,000 mty of aniline and 400,000 mty of crude MDI. Such vertical integration, wide geographic expanse, capacity to cater to different markets, versatile product functionality coupled with variable operating rates, proprietary technologies – all these strengths allow main nitrobenzene manufacturers to combat negative consequences of the pandemic and economic recession.
Find more information on the global nitrobenzene market in the in-demand research study “Nitrobenzene (NB): 2020 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2029”.
