Caprolactam is an important chemical intermediate, which is primarily used for the production of nylon 6 fibres (about 63% of caprolactam output) and nylon 6 engineering resins (about 33% of caprolactam output). Nylon 6 fibres are indispensable in textile, carpet, and industrial yarn manufacturing, while nylon resins are used in the automotive industry, electronics, specialty film packaging, wire and cabling applications, to name only a few. Caprolactam is embedded in complex and versatile production chains, which link a diverse range of upstream, intermediate, and downstream products, as well as employ multiple production routes and technologies developed by various chemical and engineering companies, like BASF, DSM, Toray, DuPont, EniChem, Sumitomo, etc.
Caprolactam-manufacturing companies can demonstrate a high level of vertical integration, both backwards and forwards. For instance, LANXESS works in a similar vein. The company produces such intermediates as caprolactam and polyamide at its Lillo/Antwerp facility, as well as engineering plastics and glass fibres. LANXESS is also an example of a responsible manufacturer with respect to ecological sustainability, which is crucial in caprolactam production. Caprolactam production can cause severe environmental issues. For instance, the operation of SPOLANA s.r.o. (Czech Republic), owned by ORLEN Unipetrol, is known to be particularly detrimental for the local environment. LANXESS operates differently. Its technology completely neutralizes nitrous oxide, associated with caprolactam manufacturing. Nitrous oxide is much more hazardous to the environment than carbon dioxide.
Apart from numerous environmental challenges, the current state of the caprolactam market is significantly affected by the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic. The European caprolactam market is an important caprolactam region. At the present time, the market functions amid a significant level of uncertainty as the seemingly receding pandemic have already exhibited a cyclic trajectory by returning via more dangerous strains. This pandemic-related uncertainty was exacerbated by technical issues at some caprolactam-producing companies, (e.g. SPOLANA and LANXESS), against the background of rising demand for caprolactam, especially in late 2020 and early 2021. It is pertinent to mention that some caprolactam-consuming sectors, like the electronic and electrical industries, are currently adversely impacted by the shortage of semiconductor chips, which acts as a huge limiting factor.
Caprolactam: structure of the global production capacity by region
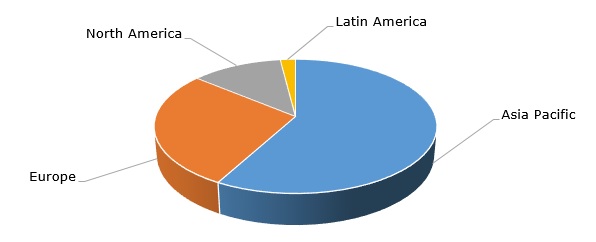
On the Indian market, which is a growing consumer of caprolactam, the situation was greatly aggravated by the pandemic, leading to an unprecedented drop in GDP, though things started to slightly improve in late H2 2021 (the country still exhibits very small vaccination rates). The Indian textile industry might also benefit from the reduction of the caprolactam import tax in this country. The robust development of the Chinese textile industry lays a strong foundation for the caprolactam sector in China. Highsun Holdings (China), which acquired caprolactam business from ChemicaInvest joint venture and manages caprolactam production via Shenyuan New Materials, Fibrant (Nanjing), and Fibrant (the Netherlands), demonstrates stable performance despite current macroeconomic challenges.
More information on the global caprolactam market can be found in the in-demand research report “Caprolactam (CPL): 2021 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2030”.
