Pumice is a rock material of volcanic origin with a variety of useful commercial applications. Being a safe and effective industrial abrasive, it is used in multiple industries, like glass making, electronics, etc. Likewise, it is applied in cleaning, polishing, and exfoliating products in the cosmetic and personal care industries. It is widely used in the construction industry (e.g., in concrete mixes, lightweight pumice concrete, grout, filler for paints, roof tiles, and other pumice-containing construction materials). Other major applications include the following: textile softening in denim fabric washing; filtration and wastewater treatment; a chemical carrier and a soil conditioner in agricultural and horticultural applications; and absorbent materials.
Major pumice-producing countries
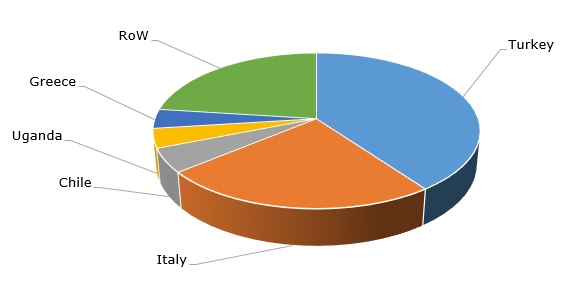
Despite the global abundance of pumice and the non-oligopolistic character of its distribution worldwide, there are very few commercial pumice deposits that are able to provide a commodity with superior chemical composition, hardness, and purity. However, the appropriate quality of feedstock is not sufficient to guarantee good long-term prospects for companies operating on the pumice market. Companies, like Hess Pumice (Idaho, US), need to extensively rely on research and innovation, while constantly adjusting their products for changing market requirements and customer specifications. With the current boom in the US construction market (in both commercial and residential segments) and multiple infrastructural projects on the way, the demand for high-quality pumice products in this country is on the rise.
The current development of the pumice market is confronted by the rising mining and transportation costs, which increased significantly in 2021. There are no signs that this trend will abate in 2022. Generally, pumice is surface mined, scraped up, and brought for different stages of processing, which implies energy-intensive activities. Another large challenge is related to environmental concerns and regulations. A vivid illustration of the latter is the operation of Pumex company, which was Italy’s largest pumice producer with 600k mty capacity (the company quarried the Mount Pelato deposit at the volcanic island of Lipari). However, in 2007 the Italian authorities closed the company factories after Pumex was accused of illegal and abusive quarrying of pumice. On the contrary, EUROPOMICE S.r.l. (Italy) has been engaged in the responsible exploitation of mineral resources over the years to gain a leading position in the production and marketing of inert volcanic materials, like pumice. In general, the state authorities can act as a very powerful stakeholder on the markets which involve mining various minerals and other resources. For instance, in an effort to improve governance and transparency in the sector of natural resources of Indonesia, the Indonesian authorities have recently announced its decision to revoke over 2000 mining permits in 2022. This may affect some local pumice producers who demonstrated ill practices.
More cutting-edge information on the global pumice market can be found in the comprehensive research report “Pumice: 2021 World Market Review and Forecast to 2030”.
