Polycarbonate belongs to a class of linear polyesters and thermoplastic polymers, which traditionally demonstrate broad variability of parameters and compositions, subject to specific and often customised requirements. Polycarbonate grades are usually subdivided into extrusion- and injection moulding-based or general-purpose and optical ones. Broad variability of polycarbonate characteristics safeguards its wide applicability. As such, it is used in such diverse areas as car-making, construction, electrical goods, electronics, optical media, piping, and healthcare, to name only a few. In general, the polymer sector, including polycarbonates, is significantly driven by technologies, innovation, and sustainability-related issues, like circular economy, recycling, and net zero GHG emissions. To illustrate the latter point, one can mention the activities of Covestro AG, which aims to reach net zero emission status and uses recycled feedstock while producing polymer materials, including polycarbonate, or the recent achievement by LG Chem, which started to export its first bio-balanced phenol and acetone for polycarbonate production. Well-known polycarbonate brands are as follows: Makrolon/Makrofol (Covestro), Lexan (SABIC), Panlite (Teijin Chemicals), Iupilon/Novarex/Xantar (Mitsubishi Engineering Plastics Corp.; as of April 2023, a part of the polycarbonate business of Mitsubishi Engineering Plastics will be absorbed by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation) and Calibre (Trinseo).
Polycarbonate: structure of the global production capacity by company
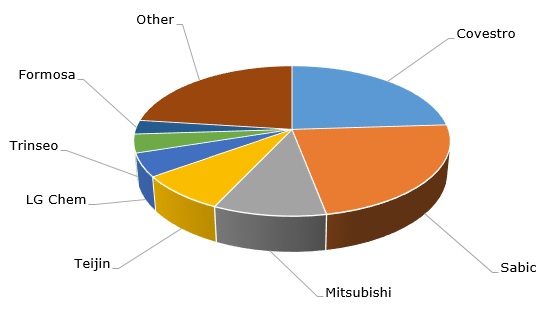
In global terms, the current polycarbonate market dynamics is characterised by a high degree of volatility and uncertainty. On the production side, soaring costs of manufacturing, energy, logistics and oil hydrocarbons, boosted prices for upstream phenol and acetone, as well as for intermediate bisphenol-A (BPA), which increased polycarbonate prices to the level that many buyers could not afford (for example, Trinseo increased polycarbonate resins prices by EUR500/mt, effective July 1, 2022). This trend is coupled with mixed demand scenarios in many polycarbonate-consuming sectors, like the automotive industry and construction, where the anticipation of the global economic recession is starting to loom large. Moreover, concerns about the global economic downturn begin to manifest with respect to all global markets, including the EU, North America and Asia-Pacific (Asia-Pacific accounts for the largest polycarbonate consumption).
Currently, the demand for polycarbonate in Asia Pacific looks soft, which increased polycarbonate supplies from Asia Pacific to Europe. There are issues across various complex value chains and distribution networks, leading to supply constraints of numerous feedstock materials and derivatives, which are not necessarily directly related to polycarbonate, but which nevertheless directly affect polycarbonate-consuming sectors, thus sending ripple effects within the polycarbonate market too. As margins of many polycarbonate producers fall, these polycarbonate producers (e.g. Trinseo, Covestro, and Sabic) have to reduce capacity utilization rates, which becomes especially evident in Q3 2022. All these factors signify that the polycarbonate market needs to adapt to the current uncertain situation and find a new supply and demand balance.
Find a detailed analysis of the global polycarbonate market in the in-demand research study “Polycarbonate (PC): 2022 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2031”.
