Polystyrene (PS) belongs to the “Big Six” group of plastics, known for its ubiquity and popularity (global PS production capacity accounts for over 15 mln mt/y as of 2022). Polystyrene popularity hinges on the following: reasonable prices, a well-balanced mix of features, excellent transparency, good mechanical properties, ease of polystyrene processing, and extensive research on the ethylbenzene (styrene) polymerization process (a key process of PS production). Therefore, polystyrene is a popular product of choice for such versatile and large-scale industries as packaging, electronics, and appliances, construction, car-making, healthcare, etc. However, this popularity comes at a cost that is inevitably associated with a larger degree of detrimental environmental impact, which poses a large challenge for the polystyrene sector.
Since plastics can adversely affect humans and ecosystems at each stage of the plastic lifecycle, all key polystyrene manufacturers have been putting significant efforts in maximising the sustainability of their manufacturing and other commercial activities. For instance, AmSty, one of the largest polystyrene producers in the Americas, prioritises sustainability and innovation (AmSty is currently a JV between Trinseo and Chevron Phillips Chemical). For AmSty, sustainability becomes an indispensable mega-trend, which goes beyond implementing traditional CSR strategies, while AmSty’s operation in this area has a systemic and all-encompassing character. The company has recently achieved the highly acclaimed “International Sustainability & Carbon Certification PLUS” recognition. AmSty is strongly committed to the principles of a circular economy and its goal to have 30% post-consumer recycled content in all of its polystyrene food packaging products by 2030. Other leading polystyrene-manufacturing companies, like Ineos Styrolution, follow the suit. Ineos Styrolution provides low-carbon, circular economy, closed-loop, and bio-based styrenics solutions and technologies. The company tries to incorporate high (up to 70% in selected grades) recycled content in its products. Usually, this process starts with assorted products, spreads across the whole range, and completes with raising the percentage of the recycled content to be used in new polystyrene-based products.
Polystyrene: structure of the global production capacity by region, 2021
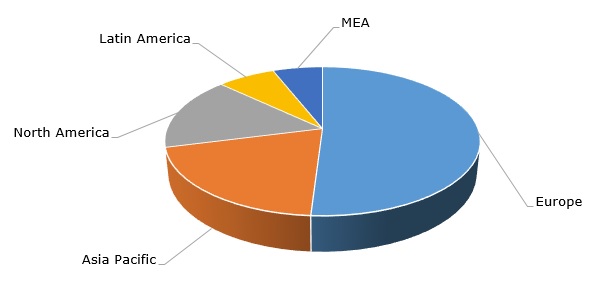
Apart from ecological concerns, the PS market is currently challenged by global macroeconomic uncertainty, very high inflation rates, supply disruptions, skyrocketed energy prices, significant volatility of feedstock costs, and demand fluctuations. In the third quarter of 2022, the European and Asian polystyrene markets demonstrated bearish expectations influenced by limited demand in many PS-consuming sectors (Europe and Asia are the world’s largest PS-producing markets). This trend dampened the PS price rise (mostly driven by feedstock cost increase) in the European and Asian PS markets. However, the US polystyrene market showed positive dynamics, supported by healthy demand for polystyrene in various sectors.
More information on the global polystyrene market can be found in the in-demand research report “Polystyrene (PS): 2022 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2031”.
