Polyisobutylenes (PIBs or polyisobutenes), including conventional PIBs (C-PIBs) and highly reactive PIBs (HR-PIBs), belong to the class of thermoplastic polymer materials (thermoplastic elastomers). They possess a range of useful properties, like excellent thermal and chemical stability, resistance to acids and salts, good flexibility at ambient temperatures, strong ability to dampen vibrations, and low gas permeability. As with all polymers, polyisobutylene can be customized to manufacture dozens of grades, for example, by controlling the polymerization conditions.
Polyisobutylene is used in a variety of applications, including the production of tires (tire inner liners and tubes), fuels and lubricants, automotive parts, adhesives and sealants, films, medical goods, food, personal care items and cosmetics, metalworking fluids, corrosion-resistant pipes, and other commodities. Polyisobutylene manufacturing involves a technically complex synthesis with the help of cationic chain growth polymerization of isobutene in methylene chloride, propene, or ethene. Polyisobutylene is marketed under various tradenames, specifically OPPANOL / GLISSOPAL (BASF), VISTANEX (formerly owned by Exxon and then purchased by BASF), INDOPOL / PANALANE (INEOS), SOLPLUS (Lubrizol) and other tradenames.
The current global polyisobutylene production capacity exceeds 1.3 mln mty. The global polyisobutylene market is worth over USD 2 billion and is mainly driven by advances in the before-alluded consumption sectors, like car making, chemical production, and fuels. The market is almost completely and equally shared between three major PIB-producing regions. Key polyisobutylene manufacturers frequently operate polyisobutylene production facilities in two or more regions. For instance, BASF produces GLISSOPAL highly reactive polyisobutylene at its facilities in Belgium, China, Germany, and Malaysia (BASF has recently introduced OPPANOL polyisobutene to the North American market). However, INEOS manufactures INDOPOL polybutene only in France (at its 80k mty facility).
Polyisobutylene: structure of the global production capacity by region
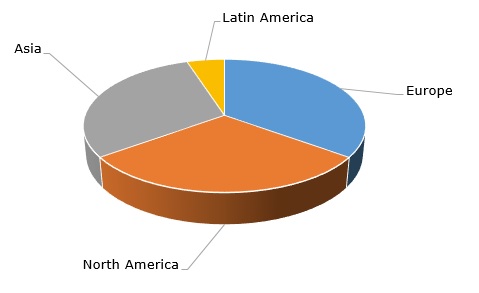
The fundamentals of the global polyisobutylene market remain strong despite recent increases in the cost of hydrocarbon feedstock, weakening consumer demand, high energy prices, logistics disruptions, and supply constraints (esp. in the automotive industry hit hard by the shortage of semiconductor chips). Demand for highly reactive polyisobutylene grades is on the rise.
Another important megatrend in the global polyisobutylene market development is sustainability when all stages of polyisobutylene production, distribution, sales, and further use can be optimised to improve sustainability, energy consumption (especially in lubricant business targeted at raising energy efficiency), water usage, and ecological footprint. Such activities became the cornerstone for the operation of key polyisobutylene manufacturers, like BASF, Infineum International (it relies on the Sustainable Portfolio Management tool developed by Solvay), INEOS, or Lubrizol.
Find more cutting-edge information on the global polyisobutylene market in the in-demand research report “Polyisobutylene: 2022 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2031”.
