Melamine (1,3,5-triaminotriazine) is a heterocyclic aromatic chemical and a triazine compound with a range of useful commercial properties. Melamine can react with formaldehyde to produce cross-linked melamine resins, which form an important class of thermosetting polymers. These melamine resins possess better mechanical and thermal properties when compared to phenolic and urea resins. Melamine resins found their application in diverse sectors, specifically as impregnation resins in furniture laminates and as glues for wood-based panels. Within these sectors, typical products for melamine application could be plywood, MDF, and particle boards. Other large sectors of melamine consumption are as follows: plastic tableware and kitchen utensils, coatings, paints, textiles, flame retardants (e.g. fire retardant polyurethane foams), leather, paper, packaging (esp. for food), automotive industry and appliances. Melamine production is dominated by Asia Pacific, which can traditionally act as an important melamine exporter to Europe.
Melamine: structure of the global production by region
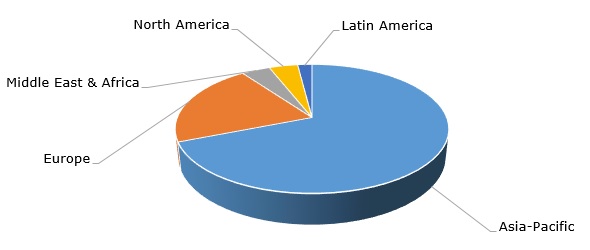
Despite its usefulness in multiple industries, melamine is often associated with tangible risks to the health of humans, pets, and ruminants, though the exact mechanism of its toxicity is not fully understood. There are numerous pathways of melamine migration into living organisms. Melamine attracted significant attention after the melamine-contaminated infant milk powder incident in China in 2008. The impact of this incident of 2008 was so great, that the trust for the Chinese dairy sector has been undermined for many years, which potentially has also affected international trade. Since then, numerous concerns have been raised in relation to melamine safety, especially with respect to its penetration into foodstuffs. This led to the establishment of stringent food safety laws, regulating melamine exposure and related food safety issues.
In late Q1 and early Q2 2023, various regional markets for melamine demonstrated similar behaviour, characterised by subdued demand, rather stable melamine prices (partially stabilized by reduced energy and feedstock prices in Q1 2023), and a large degree of uncertainty. This uncertainty also referred to seasonal fluctuations in demand for melamine as demand usually increases in the second quarter of a year. Different melamine manufacturers were uncertain if melamine market invigoration would really happen in Q2 2023, while some producers were ready to reduce melamine supply. Currently, the European market is most certainly dominated by the bearish mood, especially as BASF announced its plans to cease 65k mty melamine production at Ludwigshafen. In general, 2022 was a difficult year for melamine producers. For example, OCI (with two melamine-producing facilities in the Netherlands and China, operating a total production capacity of over 270,000 mty) reported a drop in melamine production from 132,000 mty in 2021 to 83,000 mty in 2022, though European contract price rose from EUR2000/mt in 2021 to almost EUR4,000/mt in 2022.
A detailed analysis of the global melamine market can be found in the in-demand research report “Melamine: 2023 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2032”.
