Ammonium sulphate belongs to a diverse group of sulphur-containing fertilizers. This group comprises more than twenty different commercially available fertilizers of four types. These types include fertilizers containing sulphates or elemental sulphur (or a mix of both), as well as liquid sulphur fertilisers. Sulphate-containing fertilizers (and specifically ammonium sulphate) account for about 50% of sulphur use in soils.
Ammonium sulphate is widely applied in plant nutrition for different reasons. It is a by-product of various industrial processes, especially of the caprolactam oxidation process. This raises its market availability. Its manufacturing costs are relatively low as compared to many other fertilizers, though the rise in natural gas prices, like the recent price spike, could have a dramatic effect on its supply, especially in Europe. Moreover, ammonium sulphate is indispensable for sulphur-deficient soils (in certain regions), specific crops, and peculiar tillage practices, thus providing well-balanced nutrition and sustaining high crop yields against the background of the world population growth. Owing to these benefits, global ammonium sulphate production has been growing at a steady pace over the recent years to reach 28-29 mln mty. Apart from agriculture, ammonium sulphate is used in the food industry, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, woodworking, and paper manufacturing.
However, despite these benefits, ammonium sulphate production and application in agriculture can be responsible for significant amounts of carbon dioxide and ammonia emissions, which has a tangible detrimental effect on the environment. Therefore, sustainability-focused efforts of various chemical fertilizer-producing companies in this sector are paramount. These efforts may include the implementation of measures to reduce carbon dioxide emissions across the whole ammonium sulphate production and distribution networks, the use of renewable feedstocks, and the introduction of carbon capture and sequestration technologies.
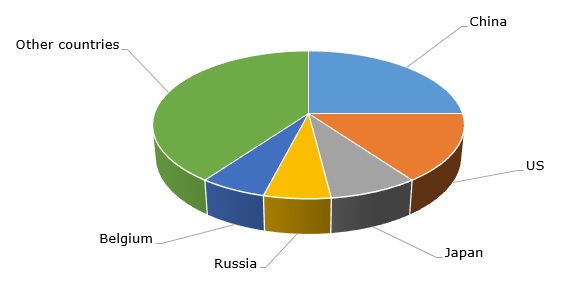
The market for ammonium sulphate is currently characterized by continued uncertainty, though positive macroeconomic signals are present too. The food and fertiliser markets are adversely affected by high inflationary pressures, global political instability, logistical disruptions, and still high, though declining, energy prices. For example, US ammonium sulphate producer AdvanSix reported worse first quarter 2023 performance as compared to the same period a year ago, blaming mostly on the complex macroeconomic situation. AdvanSix operates 1.5 mln mty ammonium sulphate production capacity and plans to expand it by 200k mty at its Hopewell, Virginia site in the future. As for ammonium sulphate production capacity at the national level, the US ranks second in the world.
Ammonium sulphate: structure of the global production capacity by country, 2022
With respect to agriculture at the start or ahead of the planting season (subject to a geographic region), the market fundamentals in Q2 2023 remain robust, which is reflected in strong crop (and ammonium sulphate) prices worldwide. The World Health Organization has recently announced that COVID-19 is no longer a public health emergency of international concern, which is a good sign for the chemical market. Such factor as weather conditions will play an important role in determining acreage allocations, crop production, and fertilizer market behaviour in 2023.
Find a detailed analysis of the global ammonium sulphate market in the in-demand research report “Ammonium Sulphate: 2023 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2032”.
