Ammonium nitrate (AN) is a salt of ammonia and nitric acid, which is extensively used as a nitrogen fertilizer. The commercial grade of ammonium nitrate contains about 33.5 percent of nitrogen. Ammonium nitrate is made mainly by the reaction between gaseous ammonia and aqueous nitric acid. The resultant ammonium nitrate solution can be used in various ways. One of them is to mix AN with a solid filler, such as calcium carbonate in various forms, to make calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN). Ammonium nitrate and calcium ammonium nitrate account for about 9% of all nitrogen fertilizers (over 112 million mty of nitrogen fertilizers is produced globally). Apart from agricultural applications, nitrogen can be used for industrial purposes.
Global nitrogen fertilizers production by country, 2022
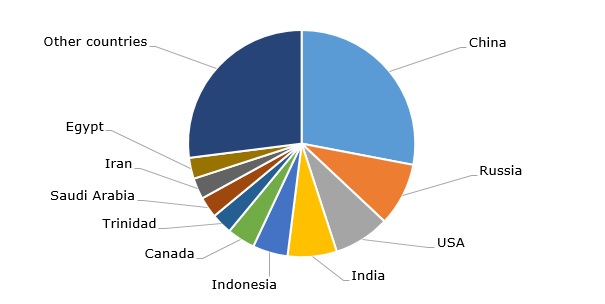
On par with two other primary macronutrients, i.e. phosphorus and potassium, nitrogen is indispensable for well-balanced plant nutrition. Irrespective of this vital role, the production and use of nitrogen fertilizers can originate a range of environmental issues, like a large carbon footprint (715 Mt CO2e in 2020) or eutrophication-contributing leaching of nitrates into groundwaters. In general, the agricultural sector is known to generate over 20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. The production of fertilizers itself also contributes to carbon footprint, though to a lesser degree as compared to their field application. Therefore, numerous AN-manufacturing companies are engaged in combating environmental issues. For example, Yara and BASF plan to launch a world-scale blue ammonia production facility with carbon capture in the U.S. Gulf Coast region. Likewise, a decarbonization strategy is pursued by another major ammonium nitrate manufacturer, CF Industries, which wants to significantly reduce its carbon footprint related to nitrogen fertilizer manufacturing. Environmental considerations together with high costs of gas influenced the recent decision by CF Industries to permanently close its ammonia plant at the Billingham Complex in the UK. In a similar fashion, Orica plans to decarbonise its ammonium nitrate production with the help of green ammonia and hydrogen.
Despite the growing issue related to excess reactive nitrogen pollution and man-caused alteration of the nitrogen cycle, the fundamentals of the ammonium nitrate market remain strong, and this trend will prevail in the future due to rising global food security concerns, especially in low- and middle-income countries. This trend has become particularly evident over the past year and a half against the background of the turbulent post-COVID life, global political instability, and volatile macroeconomics when the world market prices for both food and fertilizers increased significantly. The recent decrease (or stabilization) in fertilizer prices has been attributed to sufficient competition between firms and well-timed governmental interventions in the sector. One should not also forget that the ammonium nitrate market has been suffering from production overcapacity, despite the fact that the AN market growth rate has not been significant over the recent years. The global ammonium nitrate production stays now at around 48-49 million mty, up from about 43 million mty in 2010.
The demand for ammonium nitrate is highly susceptible to macroeconomics, seasonal factors, outlooks for new agricultural seasons, and weather conditions. For example, in summer 2023 European farmers have to operate in a very harsh environment. Parallel to high food inflation (despite some stabilization) and poorer consumption, European farmers experienced contrasting and challenging weather events in spring 2023. Of course, the fertilizer market welcomed the decrease in energy prices, but the situation remains extremely volatile. However, EU cereal production could increase in the 2023/2024 farming season, which is a good sign for ammonium nitrate as wheat is known to be the main nitrogen-consuming crop in EU countries (in the US, this role is occupied by maize).
In conclusion, the current dynamics of the ammonium nitrate market are strongly influenced by the highly volatile macroeconomic situation and uncertainties of regional agricultural seasons, which are affected by unfavourable weather patterns exacerbated by climate change. Despite these issues, numerous ammonium nitrate manufacturers are optimistic with respect to future AN market development due to its role in safeguarding food security. They also undertake significant efforts to combat various environmental problems directly and indirectly related to their ammonium nitrate-manufacturing activities.
Find a detailed analysis of the ammonium nitrate market in the in-demand research report “Ammonium Nitrate (AN): 2023 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2032”.
