Polyisobutylene (PIB) is a thermoplastic elastomer whose properties vary from an oily liquid to a rubbery material, subject to a degree of polymerization. PIB grades could be of low, medium, and high molar mass, as well as conventional and highly reactive. Its superb thermal and chemical stability, good flexibility at ambient temperature, resistance to acids and salts, vibration-dampening capacity and excellent impermeability to gases stimulate its application in various industrial and consumer commodities, such as tires, medical implants, lubricant additives, engine oils, insulating oils, adhesives, sealants, pipe encasements, chewing gum, surfactants, dispersants, surfing waxes, to name only a few. As such, polyisobutylene is consumed by the following industries: the automotive industry, construction, food packaging, electrical and electronics, the lubricant industry, sports and leisure, paints and coatings, personal care, cosmetics, and the food sector.
The modification of PIB structure and its manufacturing procedures provides large opportunities for using polyisobutylene in new and more advanced applications, such as microencapsulation (e.g. in microelectronics) and dispersion (e.g. in catalysts). Likewise, the focus on steady improvement in energy management and sustainability performance is another vital tool of any corporate strategy in the sector. For example, Chevron Oronite Company, an important PIB manufacturer headquartered in the US, has been recently awarded for excellence in energy and greenhouse gas management.
The common route for polyisobutylene manufacturing involves cationic chain growth polymerization of isobutene in methylene chloride, propene, or ethene. Polyisobutylene can be derived from 100% renewable feedstock. Popular polyisobutylene brand names are as follows: Oppanol and Glissopal (BASF), Indopol and Panalane (INEOS), and Solplus (Lubrizol). It is pertinent to mention here that BASF is known to formerly purchased several polyisobutylene businesses from various companies, such as LANXESS and ExxonMobil. These acquisitions cemented BASF’s leading position in the polyisobutylene market, followed by such companies as Lubrizol Corporation, Daelim Industrial, and TCP Group (TCP Group remains the largest PIB producer in North America). Polyisobutylenes were originally developed by BASF in the 1930s.
Polyisobutylene: structure of the global production capacity by region, 2023
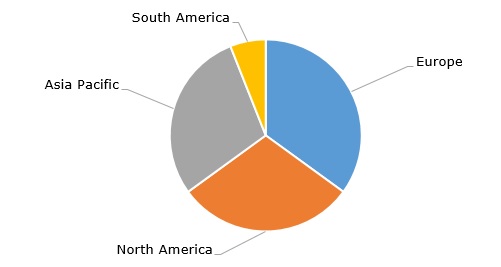
From the regional perspective, the polyisobutylene market is almost equally divided between Europe, North America, and Asia Pacific. The global polyisobutylene market is worth USD 2.5 billion, while its growth rate equals 3-4% per year and is likely to remain steady, supported mostly by demand from the automotive, construction, and a few other industrial sectors since PIB is mainly used as a fuel and lubricant additive. The growth in these sectors might be compromised if the current uncertain macroeconomic and geopolitical situation continues, which may specifically affect Europe and China.
Find a detailed analysis of the polyisobutylene market in the in-demand research report “Polyisobutylene: 2024 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2033”.
