Ethyl tertiary butyl ether (ETBE) is a popular oxygenate additive and a representative of the fuel ethers family, which also includes methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), tertiary amyl methyl ether (TAME), and tertiary amyl ethyl ether (TAEE). Being a key component of high-octane fuels, ETBE can boost gasoline performance facilitating more efficient fuel combustion and at the same time reducing automobile emissions in the environment.
When compared to other oxygenate compounds, such as MTBE or alcohols (e.g. ethanol), ETBE possesses several advantages. Ethyl tertiary butyl ether has higher values of octane rate and boiling point; it demonstrates lower values of flash point and blending Reid vapor pressure. MTBE features a higher oxygen content, but only slightly bigger than that of ETBE. Moreover, MTBE is extremely detrimental to human health and the environment, while its enhanced water solubility, as compared to ETBE, facilitates environmental contamination. Despite the existing trend of switching from MTBE to ETBE, which is, for instance, prevalent among the Japanese oil companies (such as Cosmo Oil or Nippon Oil), global MTBE production capacity significantly exceeds that of ETBE (36 mln tonnes per year vs 11 mln tonnes per year). Europe and North America account for the largest shares of ETBE production capacity.
Ethyl tertiary butyl ether (ETBE): structure of the global production capacity by region, 2023
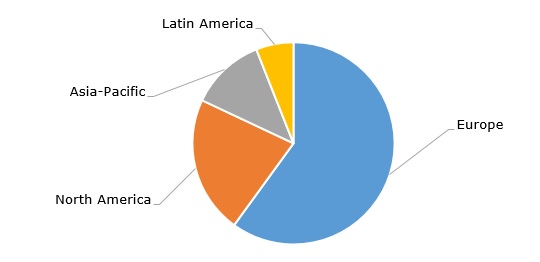
Currently, North America is privileged to occupy a better position on the ETBE market due to its access to cheaper gas, unlike Europe which has experienced significant gas price hikes over the recent time. Specifically, the attractiveness of the US market might be an important factor behind the decision of Ineos Oxide to acquire LyondellBasell’s ethylene oxide and derivatives business and a production facility at Bayport (Texas). The deal included the ethylene oxide plant, the ethylene glycol plant, and the glycol ethers plant. LyondellBasell is the second largest producer of oxyfuels worldwide, producing both MTBE and ETBE.
Ethyl tertiary butyl ether is usually produced from C4 stream hydrocarbons via the reaction of isobutene or tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) with ethanol, though the reaction conditions may vary, and different types of catalysts can be used for the reaction. In line with contemporary sustainability trends, ETBE can be produced from renewable feedstock and agricultural waste products (e.g. biomass, bio-ethanol, cellulose, etc.), which is also true for bio-MTBE, -TAME, or -TAEE. The production of bio-based oxygenates has outstanding prospects.
Find a comprehensive analysis of the ETBE market in the in-demand research report “Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (ETBE): 2024 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2033”.
