Ortho-xylene (o-xylene) is an important aromatic hydrocarbon and an essential raw material in the production of phthalic anhydride (PA) through the oxidation of o-xylene in a fluidized bed reactor. PA is in turn used to manufacture phthalate plasticizers, unsaturated polyester resins, polyols, alkyd resins, flame retardants, coatings, engineered plastics, insecticides and fungicides, pharmaceuticals, solvents, pigments, and a wide range of other commodities employed in various industries. PA can also be produced from naphthalene and renewable sources as well. The o-xylene route is known to generate PA of a higher grade as compared to the traditional naphthalene route. For example, IG Petrochemicals Limited (India) uses the o-xylene route. The company has a PA production capacity of 222,100 tonnes per year.
In general, the behaviour of the downstream phthalic anhydride market is a decisive factor in affecting demand for o-xylene. The bearish sentiment of the PA-consuming sectors, especially in the construction industry, coupled with reduced naphtha costs, safeguarded the downward trend of o-xylene prices in H1 2024. Apart from aging operational infrastructure, shrinking demand was named as one of the factors that has driven Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company (Japan) to make a decision to cease the production of o-xylene and phthalic anhydride at its Mizushima plant by the middle of January 2025.
The separation of o-xylene from other C8 isomers, namely p-xylene, m-xylene, and ethylbenzene, occurs at the modern aromatics complexes after the catalytic reforming of naphtha. Among other C8 isomers, o-xylene has the highest values of density at 20°C and boiling point and different values of melting point and relative basicity. The difference in properties facilitates C8 aromatics separation and their splitting from other fractions as the proximity of boiling points may pose a problem. The production of xylenes can be looped when the o-xylene, para-xylene, extraction, and other operational units are all linked, while the residual products (e.g. ethylbenzene) can be fed back into the system.
Demand for xylenes is estimated to exceed 50 million tonnes per year, while the existing production capacity is able to manufacture over 60 million tonnes per year. This 10 million tonne difference between annual demand and production capacity has remained constant for over a decade. O-xylene production stands at about 5.5 million tonnes per year, while Asia Pacific is a driving force of global o-xylene consumption.
O-xylene: structure of the global consumption by region, 2023
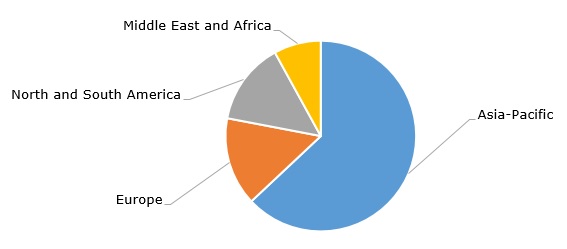
The above-mentioned use of renewables, circularity, and major decarbonization projects are the cornerstone of the current activities of key o-xylene-producing companies. For example, ExxonMobil is strongly involved in these activities in trying to reduce its carbon footprint. ExxonMobil’s Rotterdam Aromatics Plant in the Netherlands has an annual capacity to manufacture 149,000 tonnes of ortho-xylene and 775,000 tonnes of para-xylene, apart from benzene, toluene and cyclohexane. The Rotterdam Aromatics Plant is coupled with ExxonMobil’s Rotterdam Plasticizers Plant, which is able to annually convert 70,000 tonnes of PA into 420,000 tonnes of plasticizers. Vertical integration is an important element of the o-xylene-involving value chain.
Find a detailed overview of the o-xylene market in the in-demand research report “O-xylene (OX): 2024 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2033”.
