Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) belongs to a large family of polymers produced by chain-growth polymerization. It is also a fluoroplastic, which accounts for over 60% of the $4.5bn-worth fluoroplastics market. Polytetrafluoroethylene is known to exhibit high levels of crystallinity and melting temperatures. The latter prohibits its processing by standard methods typical of thermoplastics, so PTFE can be co-polymerized, for example, with hexafluoropropene to improve processibility. Apart from excellent temperature resistance, PTFE also demonstrates superb electrical insulating properties, unmatched chemical inertness, a low coefficient of friction, and incombustibility. PTFE is applied in the automotive industry, aerospace, semiconductors, electronics, household appliances, medical devices, chemical containers, wire insulation, sealing products, composite materials, eyeglasses, etc. It is produced from tetrafluoroethene (TFE) with the help of emulsion or suspension polymerization.
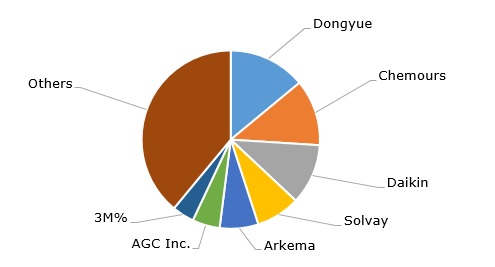
Undoubtedly, the most famous PTFE tradename is Teflon, which is known for its wide application as a nonstick coating for cookware. Teflon was initially developed and manufactured by DuPont to be later transferred to its spin-off company, the Chemours Company. Fluoropolymers manufactured by Chemours account for a significant share (about 21%) of the company’s product portfolio and 12% of the global market for fluoropolymers. Other popular PTFE tradenames include Dyneon (3M), POLYFLON (Daikin), and Algoflon (Solvay).
Major manufacturers of fluoropolymers
One of the largest challenges of the polytetrafluoroethylene market is its close association with the class of hazardous fluorosurfactants, known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which are the subject of the most stringent regulations and bans (fluorosurfactants are used as process aids in PTFE manufacturing). To illustrate the point, in 2023, Solvay’s Specialty Polymers subsidiary was a defendant in 36 separate PFAS-related lawsuits in the United States alone. 3M, the US technology company, decided to completely leave its PTFE-related business by 2025 due to such severe regulations. Other PTFE manufacturers note to the safe nature of PTFE use and want to carry on with these polymers, though they intend to fully switch to non-fluorosurfactant technologies. Solvay made a decision to convert its PTFE production to a fluorosurfactant-free mode by 2026. The tightening of the environmental legislation is currently happening against the background of a rather challenging macroeconomic situation. In this turbulent macroenvironment, the financial performance of various manufacturers of fluoropolymers during H1 2024 was worse as compared to the same period a year earlier. Many of them point to lower prices, reduced demand, and higher manufacturing expenses.
Find a detailed analysis of the polytetrafluoroethylene market in the in-demand research report “Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) 2024 World Market Outlook and Forecast to 2033”.
