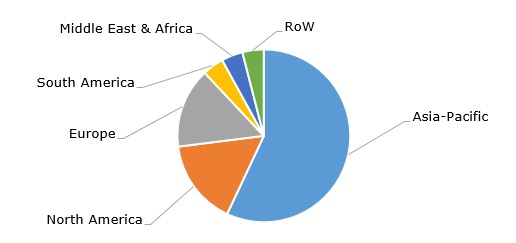
Polystyrene (PS) is an amorphous thermoplastic polymer produced with the help of the polymerization of styrene monomer and processed using such methods as injection moulding, extrusion, or thermoforming. Polystyrene, styrene monomer, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrenic specialties, and relevant styrene-based materials (e.g. polystyrene foams) are often collectively referred to as “styrenics.” Styrenic materials are among the most widely used groups of plastics after polyolefins and polyvinyl chloride. Polystyrene finds application in packaging, commercial and residential insulation, the electrical and electronics industries, lighting devices, toys, household appliances, medical goods, and other commodities and industries. Global polystyrene production capacity was equal to 15.6 million tonnes in 2023 and is forecasted to reach 16.75 million tonnes by 2026. Asia Pacific accounts for 57% of global polystyrene production capacity.
Polystyrene: structure of the production capacity by region
Polystyrene production relies on the transformation of ethylene and benzene into styrene monomer (SM) feedstock. Consequently, the dynamics of the global and regional polystyrene markets, including price fluctuations, is closely linked to the behaviour of the corresponding styrene monomer markets. For example, the spike in SM prices in Europe and North America in the summer of 2024 resulted in a rise in PS prices. Therefore, in August 2024, Trinseo, a specialty material solutions provider, increased the prices for both general-purpose polystyrene (GPPS) and high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) by EUR 135 per tonne in Europe. In August 2024, European SM prices peaked to USD 1,700/tonne FOB Rotterdam and fell to the current USD 1,090/tonne FOB Rotterdam (the U.S. spot prices for styrene monomer followed a similar trajectory). SM prices in China dropped from USD1,120/tonne FOB China in August 2024 to the current USD 1,045/tonne FOB China.
In general, the global styrene monomer market suffers from production overcapacity. For example, styrene monomer production capacity in China alone exceeds 20 million tonnes per year, and it grew by 3.7 million tonnes in 2023 (in the nearest future, the SM capacity growth rate in China will slow down but remain at 4-5% annually). SM production overcapacity transfers to the polystyrene market, which is characterised by overcapacity too, though to a lesser degree. For instance, leading U.S. manufacturers of polystyrene are currently operating at about 70% of their capacity utilization rates. This overcapacity limits prices and profit margins of both SM and PS markets. Declining demand for styrenics materials across different regions and industries, combined with increasing environmental concerns and strict ecological regulations, are prominent trends in today’s polystyrene market.
Poor economics, driven by the above-mentioned overcapacity, weaker demand, and ecological risks, is instrumental in making some major producers divest and shut down styrenics-manufacturing facilities. INEOS Styrolution intends to close its styrene-producing plant in Sarnia, Canada, by June 2026 (production capacity: 455 thousand tonnes per year), though INEOS Styrolution’s other SM-manufacturing facilities in North America (in Bayport and Texas City) remain operational. In 2022, INEOS sold its entire stake in INEOS Styrolution India to Shiva Performance Material (SPM), which is now in the process of expanding its polystyrene production capacity to 150 thousand tonnes per year at its facilities in the western Gujarat state (the expansion will be finalised by 2028). In a similar vein, the entire AmSty, which is a JV equally owned by Chevron Phillips Chemical Company LP and Trinseo, is now on sale. AmSty is a U.S.-based integrated producer of polystyrene and styrene monomer.
Find a detailed analysis of the polystyrene market in the in-demand research report “Expandable Polystyrene (EPS): 2024 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2033”.
