Polypropylene, including both propene homopolymers and copolymers, is a versatile thermoplastic polymer produced through catalytic chain-growth polymerization and used across a wide range of applications. Packaging applications account for nearly 50% of polypropylene production. Packaging is followed by consumer products (over 20%), transportation (15%), building and construction (7%), electronic and electrical goods (5%), and other commodities. Polypropylene-based injection-molded parts are widely utilized in various industries due to their durability, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, propene copolymers (e.g., ethylene-propylene copolymers) and polypropylene blends (e.g., high-impact polypropylene, created by mixing polypropylene with ethylene-propylene-diene elastomers such as EPDM) offer enhanced mechanical properties for specialized applications.
In 2024, global polypropylene consumption exceeded 86 million metric tonnes, while polypropylene production capacity worldwide was approximately 10 million metric tonnes higher. Global demand for polypropylene is projected to grow at an average rate of 2.5 to 3 million tonnes per year, with the Asia Pacific region driving the majority of this growth. This region accounts for 65% of global polypropylene demand.
Polypropylene: structure of the global demand by region
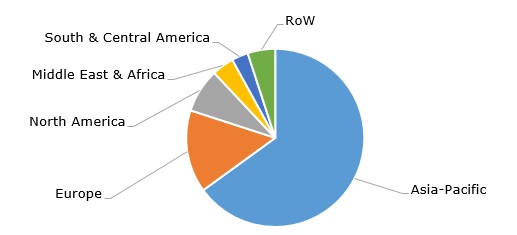
Polypropylene demand in China amounts to over 52 million metric tonnes per year, while production capacity approaches 60 million metric tonnes per year. Polypropylene is also the most widely utilized plastic in Europe, with an annual demand of over 12 million metric tonnes. Saudi Arabia has remained a top polypropylene exporter for several years. In 2021, Saudi Arabian polypropylene exports were valued at $6.4 billion.
The rate of polypropylene production capacity expansion is significant. For instance, in 2023, China increased its polypropylene production capacity by over 5.5 million metric tonnes. The general trend in China is to continue replacing polypropylene imports with local production. In India, Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd. (BPCL) plans to complete the Bina Petrochemical Refinery Expansion Project, which will include a polypropylene production capacity of 550,000 metric tonnes per year, by 2028. Additionally, BPCL aims to commission a polypropylene project at the Kochi refinery, with a polypropylene production capacity of 400,000 metric tonnes per year, by 2027.
In the coming years, various regional polypropylene markets are likely to face several interlinked challenges and pressures. These challenges may vary by region but are expected to include a global economic slowdown, aggressive expansion of production capacity, volatile feedstock prices, geopolitical and macroeconomic instability, high energy costs, tightening of environmental regulation, logistics issues, and trade barriers. Propylene price volatility, demand dynamics, and polypropylene production overcapacity result in significant polypropylene price fluctuations with vivid peaks in 2018 and 2021-2022. Polypropylene prices in 2023-2024 and early 2025 demonstrate a downward trajectory, mainly following propylene prices.
Find a detailed analysis of the polypropylene market in the in-demand research report “Polypropylene (PP): 2025 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2034”.
