Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer classified as a high-performance fluoropolymer, containing approximately 59% fluorine by weight. It exhibits a range of advanced properties, including enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance, low thermal conductivity, high thermal stability, a high melting point, outstanding chemical resistance and excellent dielectric properties. This unique combination of properties makes PVDF suitable for a wide range of industries and applications, many of which are rapidly growing or emerging (e.g. energy storage systems and renewable energy technologies).
Key sectors of PVDF consumption include electronics and radio engineering (including Hi-Fi electronics), chemical processing, biomedical and pharmaceutical industries, aviation and aerospace, metallurgy, oil and gas, food processing, paper and textiles, lithium-ion batteries (as a polymeric binder), energy storage systems for data centres, semiconductor manufacturing, automotive, water treatment membranes, nuclear power, construction (particularly in corrosion-resistant coatings), renewable energy and piezoelectric sensors, among others. PVDF-based pipes, fittings and valves are widely utilized across many of these industries. In Europe, fluoropolymer consumption is primarily driven by the transportation, chemical and power sectors, as well as electronics.
Fluoropolymer: structure of sales in Europe, by application
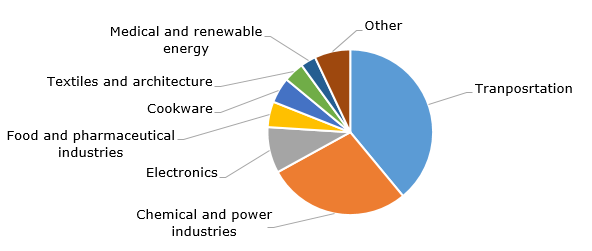
PVDF has been commercially available since the early 1960s, with the current PVDF market value exceeding USD 1.7 billion. Leading PVDF brands include KF (Kureha); Hylar and Solef (Solvay and its spinoff, Syensqo); SYGEF (GF Piping Systems); and Kynar and Kynar Flex (Arkema). Among all fluoropolymers, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) account for the largest share of consumption across various application segments. Global PVDF production capacity exceeds 230,000 tonnes per year.
According to Kureha, the EV market is currently experiencing stagnation for various reasons, particularly in Europe, leading to a decline in sales and profits in the segment related to polymeric binders for lithium-ion batteries. In Q3 2024, Kureha’s PVDF business saw a 3% decline compared to the same period the previous year. However, the company expects this segment to recover by 2026.
Kureha considers the Chinese and Japanese markets for lithium-ion batteries to be promising. Additionally, plans by the Trump administration to accelerate the development of AI, semiconductor capabilities and data centres could positively impact PVDF application in energy storage systems. The market for these systems in North America is projected to grow at an impressive annual rate of 15-30%. Kureha temporarily halted PVDF production at its Iwaki Plant from December 2024 to March 2025 as part of a project to expand production capacity at the facility. Once production resumes, the company will be prepared to supply the U.S. market with PVDF for energy storage system applications.
A similar strategic decision has been made by Arkema, which announced in February 2025 its plans to increase PVDF production by 15% at its Calvert City, Kentucky site. According to Arkema, key PVDF-consuming sectors such as lithium-ion batteries, semiconductors and cabling are expected to see strong growth.
Find a detailed analysis of the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) market in the in-demand research report “Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) 2025 Global Market Review and Forecast to 2034”.
