Diatomite (diatomaceous earth, kieselgur, or kieselguhr) is a sedimentary siliceous rock composed primarily of fossilized remains of diatom algae, known as diatoms. Its key component is silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which makes up more than 50% of its sediment weight. Diatomite has a distinctive porous structure, with a porosity exceeding 70%, as air can occupy up to 85% of its volume. It also possesses high adsorption capacity, chemical inertness, and excellent thermal stability. Due to these properties, diatomite is widely used in various applications, including filtration (e.g., in the food and beverage industry, swimming pools and biofuels), fillers, aggregates, absorbents, insulating materials, abrasive agents, mechanical insecticides, cat litter, nanocomposites, as well as biomedical, pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. It is also utilized in coatings and paints (e.g., as a matting agent), plastic films, and fertilizer processing additives (e.g., as an anti-caking agent), among many other uses. For instance, in the United States, filtration accounts for 65% of the total diatomite consumption.
The use of diatomite can contribute to sustainability efforts in several ways. It is effective in the decontamination of oil spills and can also be incorporated into construction materials to help reduce their carbon footprint, making diatomite a valuable resource from a sustainability perspective. In general, sustainability is a key priority for many diatomite-producing companies. For instance, Imerys Group, a French-headquartered company and the world’s leading diatomite manufacturer, has recently reduced its carbon footprint by 24% and aims to cut emissions by 42% by 2030, as compared to 2021 as the baseline year.
Diatomite: structure of the global production by country, 2024
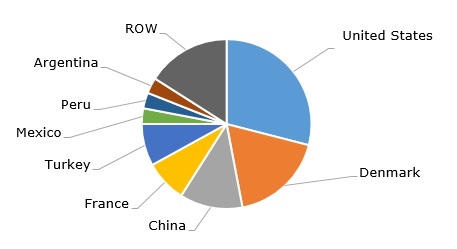
In 2004, global diatomite production exceeded 3 million tonnes per year. The United States has remained the leading diatomite producer, currently accounting for 29% of the total world production of this mineral. The U.S. share of global diatomite production has declined from 35% in 2015 to the current 29%. The country’s diatomite reserves are estimated at 250 million tonnes. National production volumes may also reflect corporate performance, as transnational corporations contribute to diatomite production in some regions. For example, Showa Chemical Industry Co. Ltd., Japan’s largest diatomite manufacturer, also operates in China. It is interesting that Japan’s diatomite production has been declining over the years. In contrast, some major manufacturers, such as EP Minerals, rely exclusively on domestic mining operations.
Diatomite is a widely available mineral mined in numerous countries worldwide. However, the centralization of diatomite production is an ongoing trend. For example, in early 2025, Imerys Group completed the acquisition of Chemviron’s European diatomite and perlite business (the acquisition included three mining and industrial sites in France and Italy). This sale of Chemviron’s diatomite/perlite assets in Europe is a reflection of Imerys’ general consolidation and expansion strategy. Imerys now operates diatomite mining and processing facilities in the United States, Mexico, Chile, Peru, France, Spain, and China. Chemviron is a subsidiary of Calgon Carbon Corporation, which was acquired by Kuraray in 2018.
Find a detailed analysis of the diatomite market in the in-demand research report “Diatomite: 2025 World Market Review and Forecast to 2034”.
