Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) is an amorphous thermoplastic copolymer. Its high degree of customization arises from the ability to adjust the ratio, morphology, and structure of its three monomeric components – acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene – allowing fine-tuning of the material’s properties. Acrylonitrile contributes primarily to chemical and heat resistance; styrene imparts gloss, rigidity, and ease of processing, while butadiene enhances performance at low temperatures. ABS polymers are produced either by blending styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymer with acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber or, more commonly and industrially preferred, through the emulsion grafting of styrene and acrylonitrile onto polybutadiene. The demand for ABS is largely driven by industries such as automotive, electronics and electrical appliances, aerospace, consumer goods (e.g., toys), and construction. These widespread applications contribute to the global demand for ABS, which accounts for about 12% of butadiene consumption worldwide.
The current global production capacity of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene exceeds 15 million tonnes per year and is projected to grow at an annual rate of 6%. However, it is common for ABS production facilities to operate at only 60-70% of their rated capacity, resulting in an actual global output of approximately 8-9 million tonnes annually.
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene: structure of the global demand by region
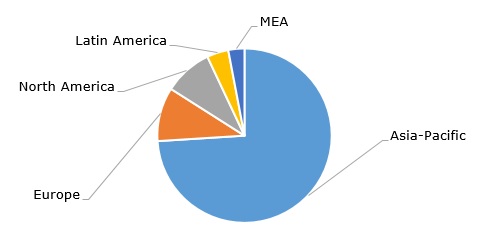
China is both the largest producer and consumer of ABS, accounting for over 40% of the global production capacity. In general, the Asia-Pacific region accounts for nearly three-quarters of global demand for ABS. China continues to expand its ABS output. For example, in 2023, INEOS Styrolution and Sinopec launched a new ABS facility in Ningbo, China. In contrast, INEOS Styrolution closed its ABS plant in Ohio, U.S., while LG Chem is entering the U.S. market by establishing an ABS compounding facility in the same state. Another notable development is the capacity expansion by Rongsheng Petrochemical and its subsidiary Zhejiang Petroleum and Chemical Co. (ZPC), in which Aramco holds a 10% stake. ZPC operates China’s largest integrated refining and petrochemical complex (the complex is located in Zhoushan, Zhejiang Province). This oversupply of ABS, particularly in China, poses challenges for manufacturers in other regions by significantly reducing profit margins.
The present global acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene market is characterized by weak demand, particularly in Europe, coupled with abundant supply. One of the key factors influencing the market is the current trade war, which has significantly increased uncertainty and made strategic business planning more challenging. These trade tensions have been further compounded by an ongoing anti-dumping investigation launched by the European Union against ABS imports from Taiwan and South Korea. South Korea, home to major ABS producers such as LG Chem, Lotte Advanced Materials, and Kumho Petrochemical, remains a significant player in the ABS market, with production reaching approximately 1.68 million tonnes in 2023. Overall, macroeconomic challenges, such as high inflation and rising geopolitical tensions, continue to exert considerable pressure on the global ABS market and ABS-consuming sectors, like electronics and car manufacturing.
Find a detailed analysis of the ABS market in the in-demand research report “Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene Copolymer (ABS): 2025 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2034”.
