Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is a non-toxic chemical compound used in a wide range of end-use sectors, namely transportation, food, cosmetics, medicine, and many other industrial applications. Ethanol or bioethanol (ethanol produced from sugarcane, corn, cassava, sweet sorghum, straw, and other biomass sources) is also a key pillar of biofuel sustainability, manifested in fuel blending, bio-based chemicals or sustainable aviation fuel. This application of bioethanol is driven by its immediate availability, ecological cleanness, and universal affordability. These features put companies, like COFCO, POET, Valero or Raízen (with Biosev S.A. as its subsidiary), at the forefront of developing bio-based energy production.
The use of ethanol-based biofuels is supported and incentivised by various policy measures (e.g., planned introduction of 20% ethanol-blended auto fuel in India in April 2023) and programmes in different countries. A vivid example of such programmes is Brazil’s National Biofuels Policy or RenovaBio program, which encourages the increase in the production of biofuels. Brazil is the world’s second-largest ethanol producer; this country is also a key biofuel producer in Central and South America.
Ethanol: structure of the global production by country, 2022
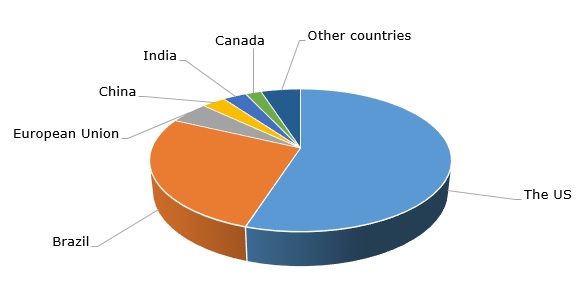
Ethanol-based biofuels have an enormous potential for transitioning to low-carbon energy systems. However, a number of serious concerns over this transition continue to exist and refer to the issues around land use changes, food security, water scarcity, biodiversity, and other environmental externalities. A different layer of concerns relates to technological and economic challenges which hamper large-scale bioethanol production (e.g., recent issues of sunliquid technology application by Clariant at its 50k mty bioethanol plant in Romania). There are also political factors which hinder the development of the bioethanol industry. For example, the US Environmental Protection Agency was instrumental in phasing out the flexible fuelled vehicle credit for automakers, which negatively affects the application of bioethanol.
Despite these concerns and barriers, the biofuel market has excellent prospects. Biofuel production is forecasted to account for 25% of total global energy consumption in the transport sector by 2050. It is stated that by 2030, ethanol has the potential to be 70% better than gasoline in terms of GHG emissions. In the current market environment of rising oil prices, often driven by political factors, bio-based ethanol could become a viable substitute. The growing demand for sanitizers and disinfectants, especially in combating various aspects of the Covid-19 pandemic, which becomes very pertinent now in the context of another Covid wave and a rising number of Covid cases in China in late 2022 and early 2023, also acts as a strong driver for the global ethanol market.
Find a comprehensive analysis of the global ethanol market in the in-demand research report “Ethanol (EtOH): 2023 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2032”.
