Sulfur is a nonmetallic element indispensable for modern chemical and other industries, acting as one of the most fundamental chemical building blocks. Manufacturing agricultural fertilizers, like phosphates and ammonium sulphate, is a main outlet for sulfur in the form of sulfuric acid. Other key applications include its usage in the production of electric motors, lithium-ion batteries, metals, polymers, pharmaceuticals, explosives, semiconductors, paper, soaps, and detergents, to name only a few. For example, Chemtrade (Canada), which is one of North America’s largest suppliers of sulfuric acid and a leading regional supplier of sulfur, states that its sulfur-related products contribute to dozens of industries. It is pertinent to mention that sulfur production has long been a symbol of national economic strength due to its role in making ammunition. Sulfuric acid is also essential in the extraction and refining of ferrous and nonferrous metals, which often determines the availability of sulfur and makes it regularly dependent on the operational schedules of smelters and metal market macroeconomic factors.
Currently, in an effort to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide and to protect valuable catalysts used in the petrochemical industry, desulfurization of fossil fuels (mainly from natural gas and oil refining industries) accounts for over 80% of the global sulfur supply. At the same time, the continuous curtailment of fossil fuel consumption to address the most pressing long-term climate challenges is a global megatrend. The realization of this trend may produce a shortage of sulfur and sulfuric acid, the demand for which may rise from the current 250 million tons to 400 million tons by 2040 (the sulfur-to-sulfuric acid conversion rate is approximately 1 to 3). This shortage may be evident despite seemingly limitless reserves of elemental sulfur and sulfate minerals. In general, sulfur is ubiquitous, which significantly demonopolizes its market. However, the possible sulfur shortage, ensuing in the case of decarbonization, may have a detrimental impact on global agriculture and other green technologies, and generate vulnerabilities for different nations, especially developing ones.
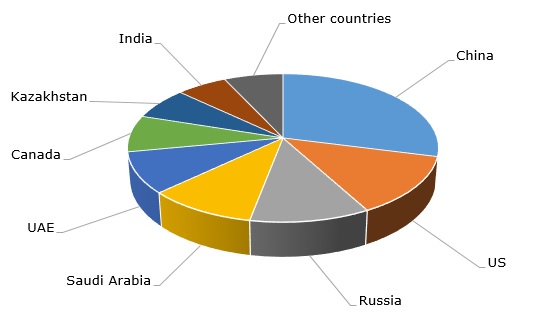
Sulfur: structure of the global production by country, 2021
Likewise, an interesting development may come from the appeals of various countries (e.g., India) to cut the use of synthetic fertilizers. To a certain extent, this runs counter to the pledges on the corporate level to boost fertilizer production. For example, OCP Group (Morocco) has recently adopted an investment program, which aims to increase fertilizer production capacity from the current 12 million tons to 20 million tons by 2027. As for the most recent developments on the sulfur market, this market in early Q1 2023 remained bearish, driven by the lack of demand in the downstream sectors and sulfur oversupply. Such oversupply has always been evident, stabilizing the price of sulfur at the international markets.
Find a detailed analysis of the global sulfur market in the in-demand research report “Sulfur: 2023 World Market Review and Forecast to 2032”.
